Gout
What is Gout?
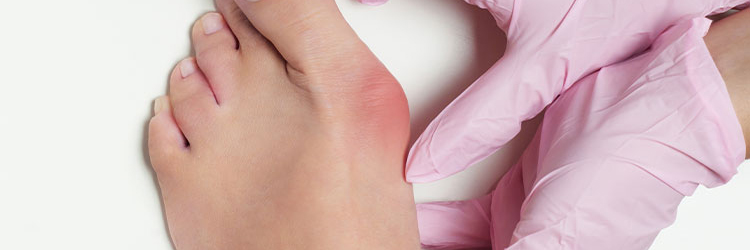
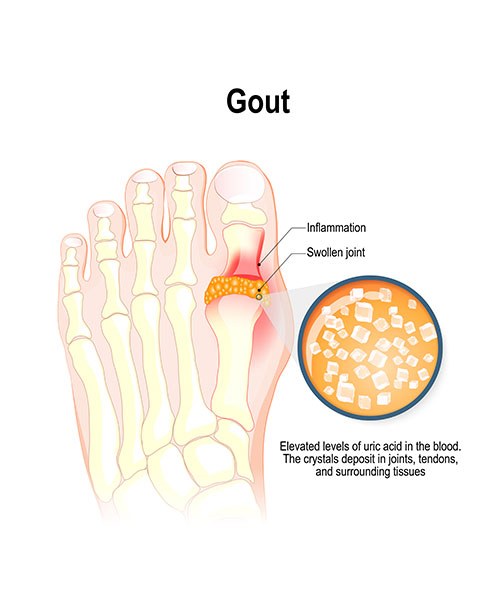
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that occurs when high levels of uric acid in the blood cause crystals to form and accumulate in the joints. The excess uric acid can come from the body’s overproduction of uric acid or from the body’s inability to excrete uric acid properly. Gout typically affects the joints in the lower extremities, such as the big toe, ankle, and knee. Symptoms of gout can include sudden and severe pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint. Gout attacks can be triggered by factors such as alcohol consumption, certain foods (such as red meat, seafood, and sugary drinks), and certain medications.Gout is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to measure the levels of uric acid in the blood.
How do you treat Gout?
Gout can be treated with a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. The main goals of treatment are to relieve acute pain and inflammation associated during gout attacks, and then to prevent future gout attacks, and reduce the levels of uric acid in the blood. Medications commonly used to treat gout include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation during gout attacks.
- Colchicine: This medication can also help relieve pain and reduce inflammation during gout attacks.
- Corticosteroids: These medications can be given orally or injected into the affected joint to reduce inflammation during gout attacks.
- Uric acid-lowering medications (ex. allopurinol or febuxostat) : These medications are used to prevent future gout attacks by reducing the levels of uric acid in the blood. Examples of uric acid-lowering medications include allopurinol and febuxostat.
In addition to medications, lifestyle changes can also help manage gout. These may include:
- Limiting alcohol intake: Alcohol can increase the levels of uric acid in the blood and trigger gout attacks.
- Eating a healthy diet: A diet low in purines (found in red meat, organ meat, and some seafood) and high in complex carbohydrates (found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables) may help reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out excess uric acid from the body.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight can increase the risk of gout and may make gout symptoms worse.
It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan for gout. In severe cases of gout, joint damage and deformity can occur, so early diagnosis and treatment is important in managing gout effectively. See your podiatrist at PS Foot and Ankle in Bridgewater, NJ.
What foods should I avoid if I have Gout?
If you have gout, it is important to avoid foods that are high in purines, as these foods can increase the levels of uric acid in the blood and trigger gout attacks. Foods that are high in purines include:
- Red meat: Beef, pork, and lamb are all high in purines.
- Organ meat: Liver, kidney, and other organ meats are high in purines.
- Seafood: Certain types of seafood, such as anchovies, sardines, mussels, and scallops, are high in purines.
- High-fructose corn syrup: Foods and drinks that contain high-fructose corn syrup, such as soft drinks and some fruit juices, can increase the levels of uric acid in the blood.
- Alcohol: Beer and hard liquor, in particular, can increase the risk of gout attacks.
It is also a good idea to limit your intake of foods that are moderately high in purines, such as poultry, fish, and some vegetables (such as asparagus, spinach, and mushrooms). Instead, focus on eating a healthy diet that is low in purines and high in complex carbohydrates (found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables). Drinking plenty of water can also help flush out excess uric acid from the body.